The world is an interesting place. It’s like a sandbox simulator where opportunity collides with chance, and the tiniest twist in circumstance can catch you completely off guard.
The Facebook page ‘Yup That Exists’ collects some of the most unexpected things that have emerged throughout history, from peculiar inventions to odd social customs. Their posts make you laugh, smile, or scratch your head, and a few are so bizarre you might even start worrying a little about the future.
Just when you think you’ve seen everything on the internet!
More info: Facebook
#1

Image source: yupthatexists
#2

Image source: yupthatexists
#3

Image source: yupthatexists
#4

Image source: yupthatexists
#5
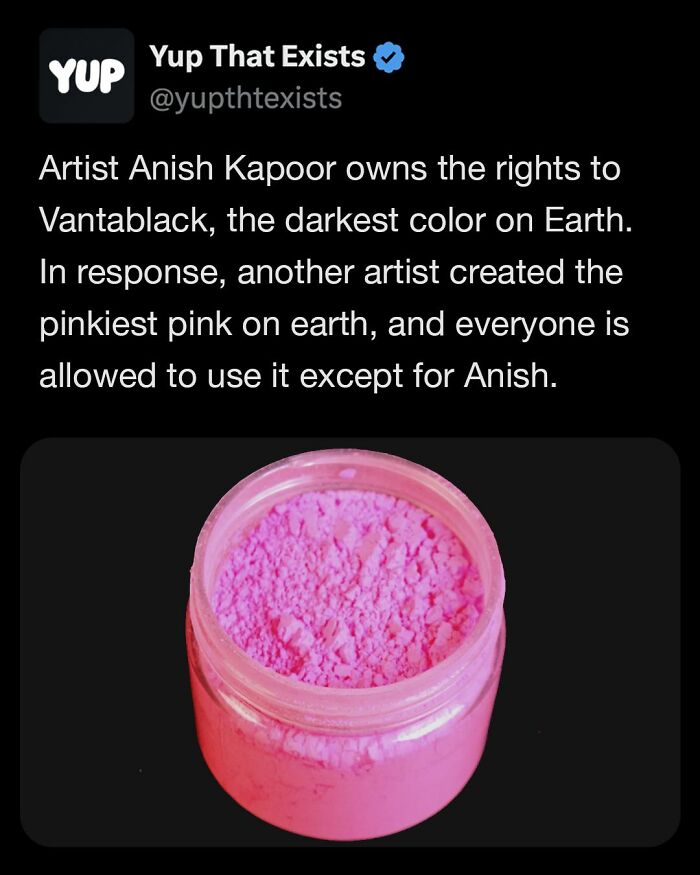
Image source: yupthatexists
#6

Image source: yupthatexists
#7

Image source: yupthatexists
#8

Image source: yupthatexists
#9
In Augsburg, Germany, you can live in a real-life medieval village for less than a euro a year. The Fuggerei, founded in 1521 by wealthy banker Jakob Fugger, is the world’s oldest social housing complex still in use.
Residents pay around ~$1.00 a year and follow simple community rules including volunteering and daily reflection. The walled village survived wars, bombings, and centuries of rising rents, yet it still houses 160 people who might otherwise be priced out of the city.
With its cheerful yellow terrace houses, locked gates at night, and a steady stream of tourists, the Fuggerei isn’t just a home, it’s a living lesson in history, generosity, and the power of affordable housing.
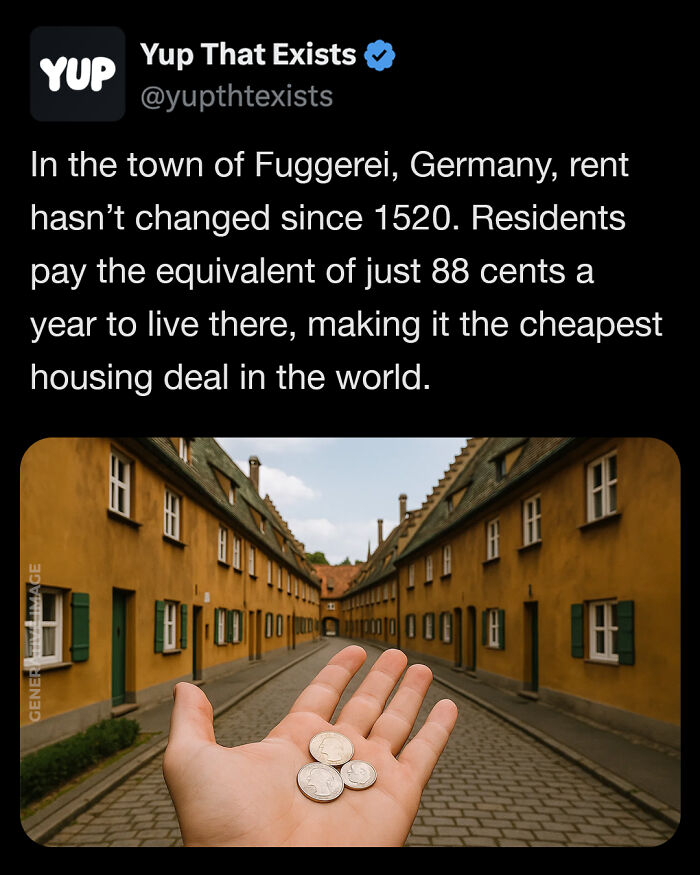
Image source: yupthatexists
#10
In a historic legal move, a New York court has made dogs official “immediate family members” in a case involving emotional distress.
This groundbreaking decision comes after a woman witnessed her dog being struck and k**led by a car while leashed to her body. For the first time, the court allowed a negligent infliction of emotional distress claim for the death of a pet, something previously reserved for human relatives.
While the ruling is under appeal and remains specific to this case, it raises big questions about how the law views the bond between humans and animals. But not everyone’s on board; veterinary groups are concerned that recognizing pets in this way could lead to higher liability costs and even impact veterinary care prices.
As this case progresses, it’s pushing us to rethink how we value the relationship between people and their pets.

Image source: yupthatexists
#11

Image source: yupthatexists
#12
In Japan’s Ako City, vending machines have leveled up for emergencies.
When an earthquake or severe disaster strikes, they automatically unlock, giving people free access to food, water, and survival gear.
These machines are packed with drinks, instant meals, masks, and even portable toilets, making sure communities have what they need when disaster hits.

Image source: yupthatexists
#13

Image source: yupthatexists
#14

Image source: yupthatexists
#15

Image source: yupthatexists
#16

Image source: yupthatexists
#17

Image source: yupthatexists
#18

Image source: yupthatexists
#19
Japanese researchers at the University of Tokyo have created contact lenses that give users night vision without batteries, wires, or external cameras.
The lenses use graphene-based sensors to detect infrared light, the kind of heat emitted by humans and warm objects, and convert it into visuals directly on the retina. They’re ultrathin, flexible, and powered by body heat and blinking motion.
Early tests show wearers can spot people, hidden objects, and heat leaks even in total darkness. Beyond night vision, the tech could help doctors see blood vessels or inflammation without invasive tools, opening the door to a whole new level of enhanced sight.

Image source: yupthatexists
#20

Image source: yupthatexists
#21
Science has just confirmed what dog lovers have always known deep down, your dog loves you more than food!
A groundbreaking fMRI study by neuroscientist Gregory Berns at Emory University has shown that when dogs smell their owners, the caudate nucleus in their brain, which controls joy, reward, and affection, lights up more than when they smell food or even other dogs.
This means your scent doesn’t just feel familiar to them; it triggers an emotional response tied to love and bonding. It’s official, you’re not just a caretaker to your dog; you’re family!
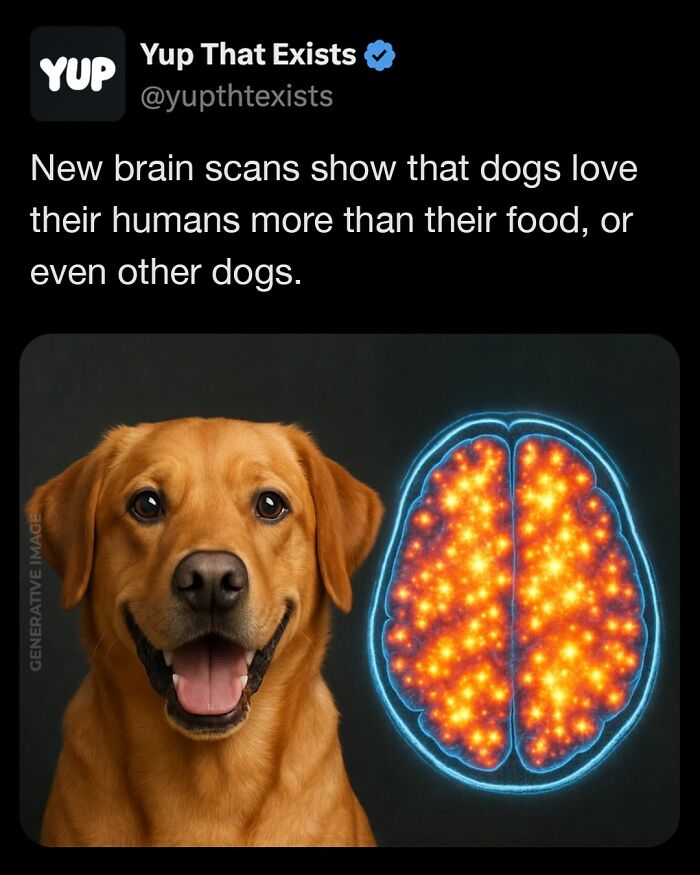
Image source: yupthatexists
#22

Image source: yupthatexists
#23
A new toothpaste made from human hair protein could actually rebuild your tooth enamel and stop decay in its tracks.
Scientists at King’s College London have developed a keratin-based formula from human hair and wool that forms a dense, enamel-like coating on teeth. Lab tests show it not only restores lost enamel but also seals nerve channels, reducing sensitivity and protecting against further erosion.
Unlike fluoride, which just slows enamel loss, this protein-packed toothpaste actively repairs damage and offers a natural, eco-friendly alternative to traditional dental resins. It could hit shelves in as little as two years as a daily toothpaste or professional gel treatment, turning everyday hair and wool waste into a revolutionary dental solution

Image source: yupthatexists
#24

Image source: yupthatexists
#25
Crown shyness is a strange and beautiful phenomenon where the tops of certain trees avoid touching each other, creating narrow gaps in the forest canopy.
While the exact reason is still debated, scientists believe it may help trees reduce damage from branches colliding in the wind, prevent the spread of pests, or allow more sunlight to reach lower leaves and the forest floor.
The result is a striking, puzzle-like pattern overhead, almost like the trees are giving each other personal space.

Image source: yupthatexists
#26
Norway has just unveiled a revolutionary damless river turbine that generates clean power without blocking water. This cutting-edge technology, installed in the Suldalslågen River, uses a submerged turbine suspended in the flow of water to transform kinetic energy into electricity.
Designed like a modern water mill, it silently spins with the current, converting power through submerged cables to a floating platform. The best part is that it’s eco-friendly! Fish can swim right through it without harm, and it doesn’t require any excavation or alteration of the riverbed.
Operating 24/7, even under ice, each turbine can power up to 10 homes, and hundreds of them could be linked to create a decentralized power network. Norway’s groundbreaking invention is paving the way for a future where clean, affordable energy can be harnessed from rivers without damaging ecosystems or migrating species. Energy without the destruction—this is the future of hydroelectric power.

Image source: yupthatexists
#27

Image source: yupthatexists
#28

Image source: yupthatexists
#29

Image source: yupthatexists
#30

Image source: yupthatexists
#31

Image source: yupthatexists
#32
Meet the Alaskan wood frog, a tiny creature that can survive being completely frozen during winter. Its heart stops, it stops breathing, and even its brain shuts down, yet it somehow lives.
Researchers at the University of Alaska Fairbanks discovered that the frog floods its body with glucose and urea to shield its organs from ice damage. When spring arrives, it thaws and hops back to life as if nothing happened.
Scientists are studying this incredible survival trick to explore new possibilities in medicine and preserving living tissue.

Image source: yupthatexists
#33
Luxembourg is making history by becoming the first country in the world to offer free public transport on buses, trains, and trams everywhere.
This bold move makes getting around easier for everyone, encourages people to leave their cars at home, and tackles traffic jams and carbon emissions.
The country is now leading the way in creating greener, more sustainable cities that others around the world might soon follow.

Image source: yupthatexists
#34

Image source: yupthatexists
#35
Say hello to the future of batteries. Canada has just developed an eco-friendly battery made from tree pulp that powers small devices and biodegrades entirely in soil.
With no toxic metals and no e-waste, this innovative battery is completely compostable within 60 days, leaving no environmental footprint behind.
It’s a breakthrough that could change the way we think about energy storage and waste. Could this be the key to a cleaner, greener future?

Image source: yupthatexists
#36

Image source: yupthatexists
#37
Being around someone you truly trust doesn’t just make you feel good, it changes your body too.
Your brain releases oxytocin, a hormone that eases stress and helps you relax, slowing your heart rate and even making you feel sleepy.
Research shows couples can actually sync up while they sleep, with heartbeats and movements aligning throughout the night. Love doesn’t just calm your mind, it can literally reshape the way you rest.
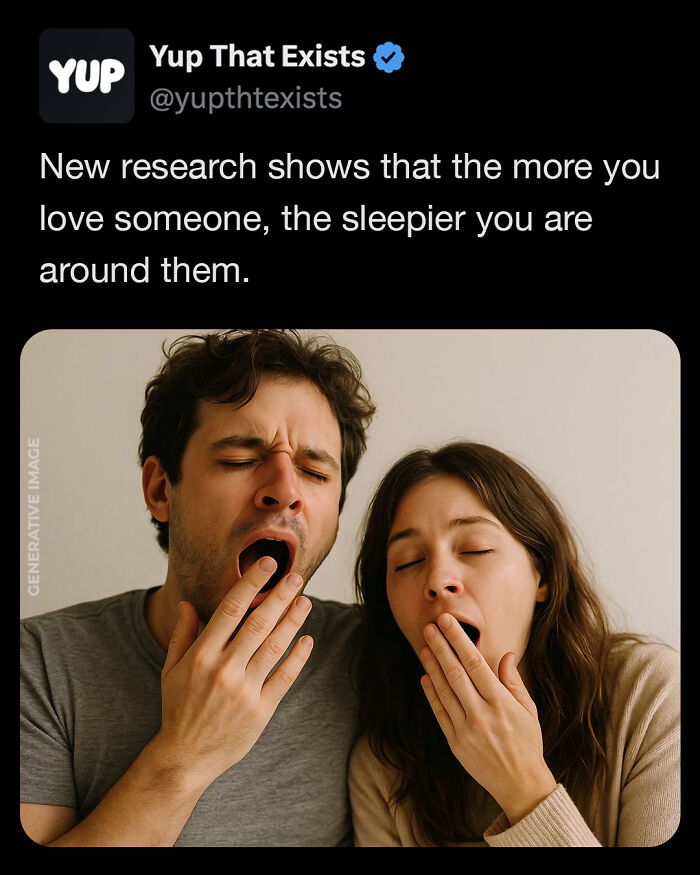
Image source: yupthatexists
#38
A single dose of an experimental cell therapy caused a woman’s aggressive brain tumor to nearly disappear in just five days. At Mass General Cancer Center, three patients with glioblastoma, one of the deadliest and most treatment-resistant cancers, saw their tumors shrink within days of one infusion.
One tumor vanished almost completely, another dropped by over 60% and stayed that way for six months. The treatment reprograms a patient’s own immune cells to attack multiple targets inside the tumor at once, a breakthrough for cancers that usually dodge single-target therapies.
While the tumors eventually returned, the rapid and dramatic results are unlike anything researchers have seen before, and scientists are now racing to make the effect last and maybe one day cure this devastating disease
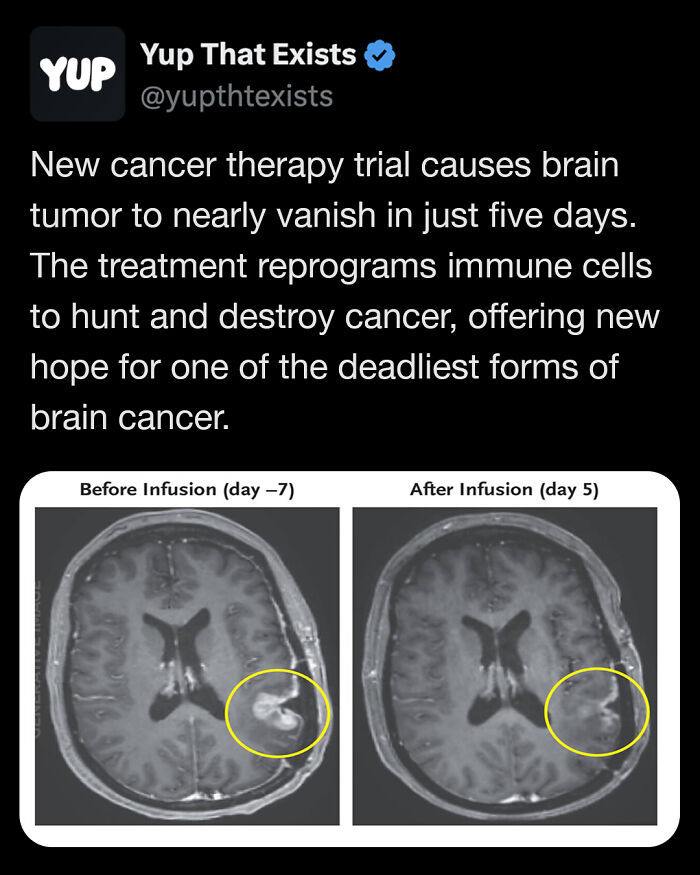
Image source: yupthatexists
#39
Scientists exploring the radioactive ruins of Chernobyl have uncovered a surprising survivor: fungi that don’t just survive radiation, they thrive on it.
Species like Cladosporium sphaerospermum and Cryptococcus neoformans use a process called radiosynthesis to convert dangerous gamma rays into energy, thanks to the melanin in their cells. These fungi even grow toward radiation, tolerating levels hundreds of times higher than normal.
Researchers are now looking at how these radiation-eating organisms could help clean up contaminated sites on Earth or protect astronauts from cosmic radiation on long space missions. The discovery shows just how adaptable life can be and hints at some wild possibilities for environmental science and space exploration.

Image source: yupthatexists
#40

Image source: yupthatexists
#41

Image source: yupthatexists
#42
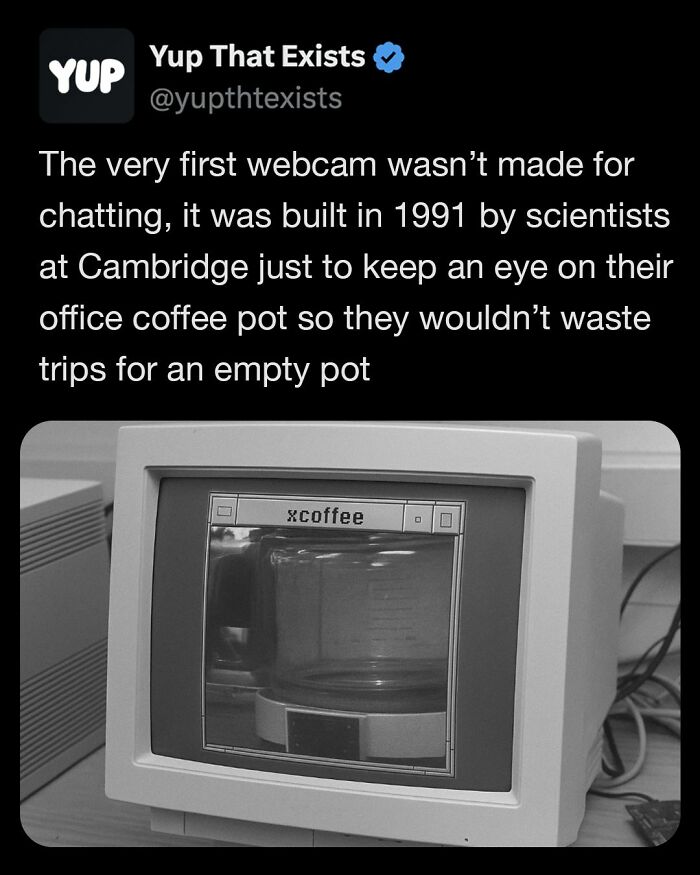
Image source: yupthatexists
#43
Fungi might look like quiet forest dwellers, but new research suggests they could be secret communicators.
Scientists at the University of the West of England found that electrical signals traveling through fungal networks show patterns surprisingly similar to human speech.
By inserting tiny microelectrodes into the mycelia of enoki, split gill, ghost, and caterpillar fungi, researchers discovered clusters of spikes that form “vocabularies” of up to 50 words.
Split gills, which grow on decaying wood in wavy coral-like formations, produced the most complex “sentences.” These electrical bursts may help fungi coordinate growth, share information about food sources, or simply maintain their network’s integrity.
While the idea of talking fungi is exciting, scientists caution that more research is needed before calling it a true language. Even so, the discovery opens a fascinating window into how life communicates in ways we are only beginning to understand

Image source: yupthatexists
#44

Image source: yupthatexists
#45
In Hong Kong, a new light sensor technology is revolutionizing street lighting. Street lamps now feature smart sensors that detect the movement of pedestrians, cyclists, and vehicles.
When the streets are empty, the lights automatically dim to save energy, and as soon as someone approaches, they brighten instantly to ensure safety. This system not only cuts down on electricity use but also helps reduce carbon emissions and operational costs.
Hong Kong’s dense population has traditionally led to high energy consumption for street lighting, but with motion-activated lights, the city is making strides toward a more sustainable future without sacrificing safety.
Additionally, the dimming feature helps reduce light pollution, protecting the natural night sky and minimizing glare. This innovative approach is part of Hong Kong’s larger smart city efforts, combining energy efficiency and digital technology to create a more livable, eco-friendly urban environment

Image source: yupthatexists
#46
In a wild twist of fate, Diesel the donkey has been found living among a herd of wild elk near Cache Creek in Northern California, four years after going missing.
Back in 2019, Diesel bolted from the trail during a hike, and despite an extensive search by his owners, Terrie and Dave Drewry, they eventually gave up hope. Fast forward to 2024, and hunter Max Fennell captured footage of a donkey grazing alongside more than ten elk.
When the video went viral, the Drewrys instantly recognized Diesel, confirming it was him, as wild donkeys aren’t found in that area. Diesel, now healthy and thriving, has fully integrated into the elk herd, grazing with them and even acting as a protector against predators like coyotes and mountain lions

Image source: yupthatexists
#47
In Japan, a curious service called “johatsu,” meaning evaporation, lets people vanish from their lives completely and legally.
Entire companies specialize in helping people disappear by moving their belongings under cover of night, wiping digital traces, and even creating new identities in distant locations.
Some use it to escape debt, a***ive situations, or the pressure of social judgment while others simply crave a fresh start free from family, work, or society’s expectations.

Image source: yupthatexists
#48
Plants are secretly chatting right under our noses. Scientists discovered that houseplants use roots and airborne signals to form a hidden network, sometimes called the wood wide web.
Through this underground and overhead system, they warn each other about pests, drought, and stress while sharing resources to survive.
Even more surprisingly, plants can tell different humans apart and change how they react to care. Your living room is not just for decoration, it’s a buzzing community of plant communication

Image source: yupthatexists
#49

Image source: yupthatexists
#50
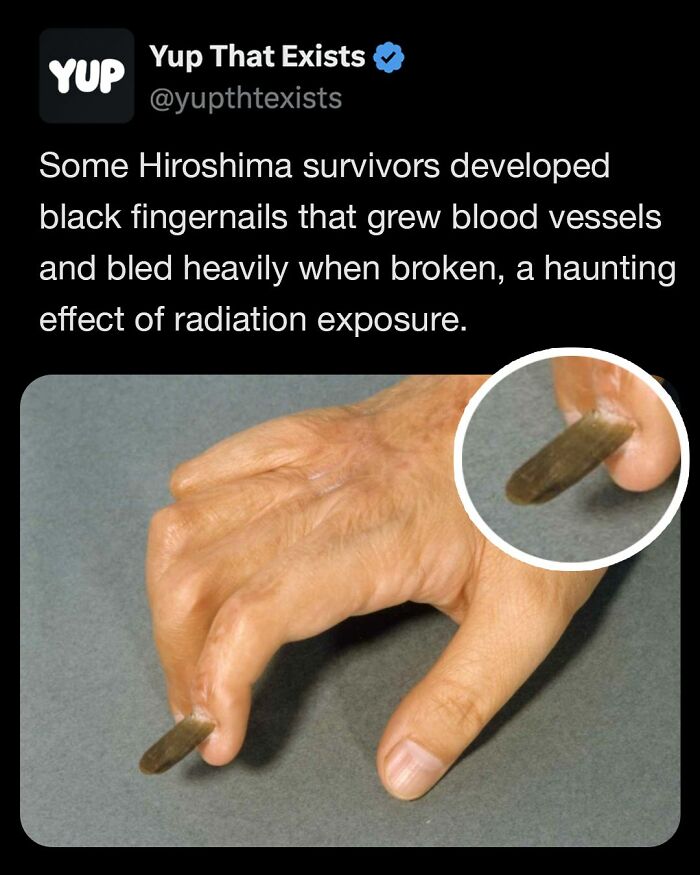
Image source: yupthatexists
#51

Image source: yupthatexists
#52

Image source: yupthatexists
#53
Blue whales are going quiet, and it’s raising major concerns among researchers. A recent study from Cornell University’s K. Lisa Yang Center for Conservation Bioacoustics found that blue whale songs have dropped by nearly 40% in recent decades.
These songs are crucial for communication, mating, and navigation, so this decline is alarming. Scientists suggest that the quieter whales are a result of starvation and ecosystem disruption caused by warming oceans and shrinking krill populations.
With less energy to spend on vocalizing, these changes might be a sign of a broader environmental crisis in our oceans.

Image source: yupthatexists
#54

Image source: yupthatexists
#55

Image source: yupthatexists
#56

Image source: yupthatexists
#57

Image source: yupthatexists
#58
In Germany, old coal mines are getting a second life as huge underground parks, transforming former symbols of pollution into spaces for nature, culture, and recreation.
Abandoned tunnels are now being turned into walking trails, cycling paths, art galleries, and even botanical gardens, all illuminated with advanced LED systems. With the naturally stable underground climate, these parks are perfect for year-round activities, rain or shine.
Some projects even use geothermal heating from the old mine shafts, making them energy-efficient and eco-friendly. Not only do these parks preserve the region’s industrial history, but they also help revive post-mining communities by attracting tourists, creating jobs, and boosting local economies

Image source: yupthatexists
#59
A fascinating find for cheese lovers and history buffs alike: the University of Leeds has transcribed an English book on cheese that dates back to the 1580s!
The book, titled A pamflyt compiled of Cheese, was purchased at auction in 2023 and offers some unexpected rules about cheese consumption.
For example, the author warns that drinking dog’s milk could cause premature birth (yikes!). Camel, mare, and donkey milk cheeses, on the other hand, seem acceptable, but human milk definitely isn’t on the menu.
The book also discusses the best time to eat cheese (at the end of a meal for optimal digestion) and whether it’s okay to eat during religious events, considering the use of animal rennet.
This text is one of the earliest known studies on cheese, looking at its effects on the body and when and how it should be consumed. Food historian Peter Brears even called it “probably the first comprehensive academic study of a single foodstuff written in the English language.”

Image source: yupthatexists
#60
MIT engineers have developed a groundbreaking water harvester that taps into the atmosphere to provide clean drinking water, even in dry areas like Death Valley.
This device uses a unique, origami-inspired hydrogel material that absorbs moisture from the air at night and releases it during the day using sunlight. The panel, about the size of a window, operates completely without power, making it ideal for remote regions with limited access to electricity.
In Death Valley, it produced up to two-thirds of a cup of water per day, even in low humidity conditions. With its efficient, scalable design, this innovation could be a game-changer in addressing the global water crisis, providing a reliable source of fresh water in arid environments.

Image source: yupthatexists
#61

Image source: yupthatexists
#62
Scientists may have found a surprising new starting point for Parkinson’s disease. A study from Wuhan University suggests that the kidneys, not the brain, could be where the trouble begins.
Researchers discovered clusters of alpha-synuclein proteins in the kidneys of Parkinson’s patients. Experiments in animals showed that healthy kidneys could clear these proteins, but when kidneys malfunctioned, the proteins built up and traveled to the brain, causing damage.
The study also spotted protein buildup in people with chronic kidney disease even when there were no brain symptoms, hinting that the kidneys could be an early hotspot for the disease. While still early research, this could change how scientists approach Parkinson’s prevention and treatment
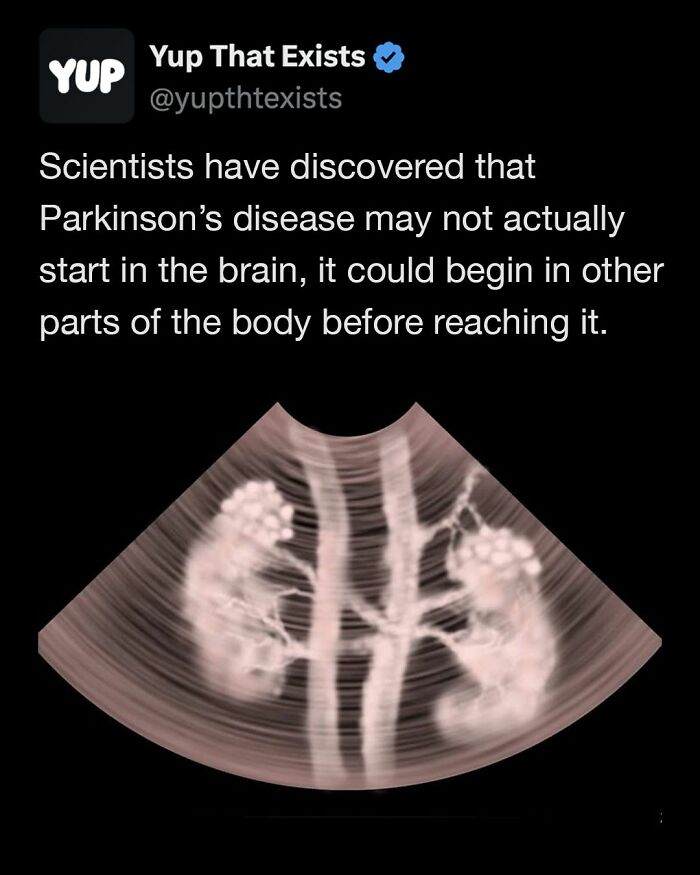
Image source: yupthatexists
#63
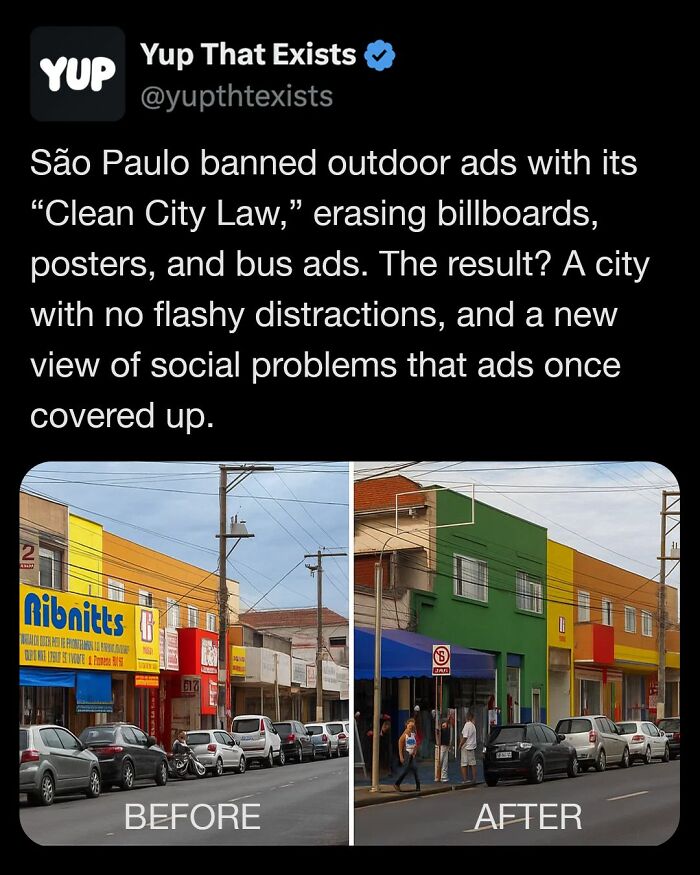
Image source: yupthatexists
#64
Princeton researchers recently discovered that human brains emit ultra-low-frequency electromagnetic waves that link into a global neural network.
These signals are capable of subtly influencing other people’s brains from up to 10,000 kilometers away, suggesting human consciousness may be quietly interconnected across the planet.
This finding builds on a growing body of research showing that our brains communicate not only through neurons but also through weak electromagnetic fields. Some studies suggest these fields could play a role in empathy, intuition, and synchronized behavior in groups.
Experiments have even hinted that when one person focuses or meditates, nearby or even distant individuals may show small changes in brainwave patterns, hinting at a hidden layer of human connection we’re just beginning to understand
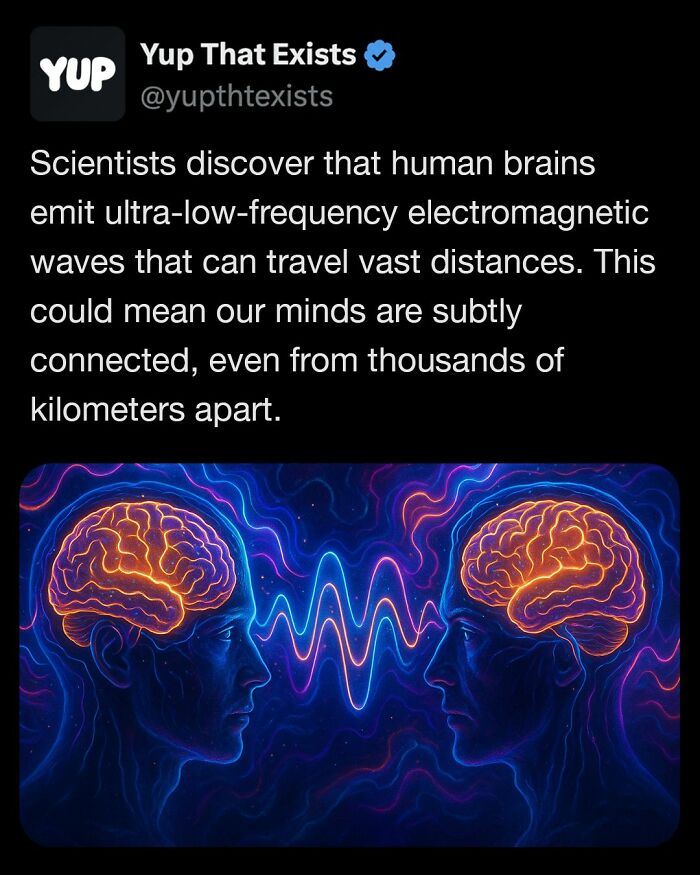
Image source: yupthatexists
#65
Over 200 years ago, people believed tetanus was a sign of demonic possession because patients would convulse, stiffen, and arch their bodies in extreme ways.
Back then, no one knew the real culprit was a bacterium called Clostridium tetani, which attacks the nervous system and triggers painful muscle spasms.
By the 19th century, scientists uncovered the true cause and swapped the supernatural theory for real science.

Image source: yupthatexists
#66
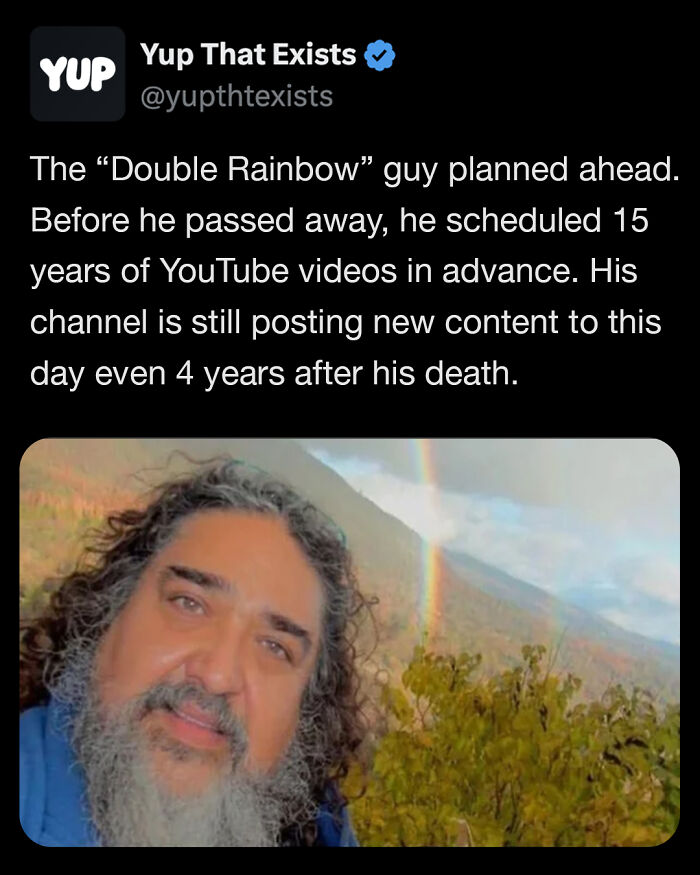
Image source: yupthatexists
#67
Engineers at Boston University have developed a groundbreaking robotic system that could change the future of aircraft maintenance. This tiny, insect-sized drone is designed to inspect and repair aircraft skin while the plane is still in the air.
Weighing just 95 grams, the robot uses AI to scan for microfractures and apply a special adhesive to fix any damage mid-flight. The drone is stored in the fuselage and can fly along the plane’s surface, detecting and sealing cracks with precision.
During tests on a modified Boeing 727, the robot successfully patched up minor cracks at 20,000 feet with no disruption to the flight. With the potential to reduce maintenance downtime by over 60%, this innovation could save airlines and defense contractors a lot of money.

Image source: yupthatexists
#68

Image source: yupthatexists
#69
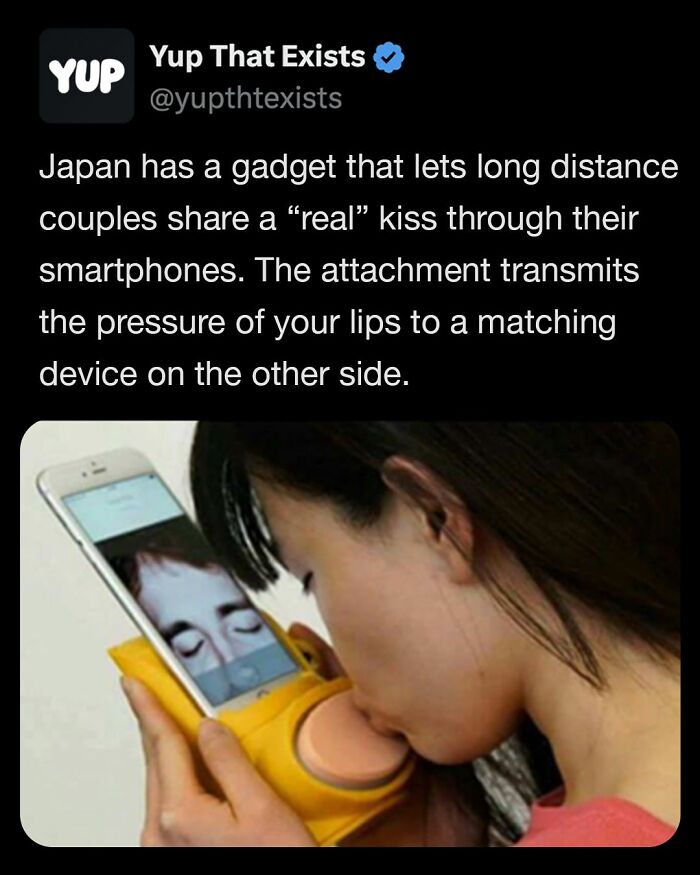
Image source: yupthatexists
#70
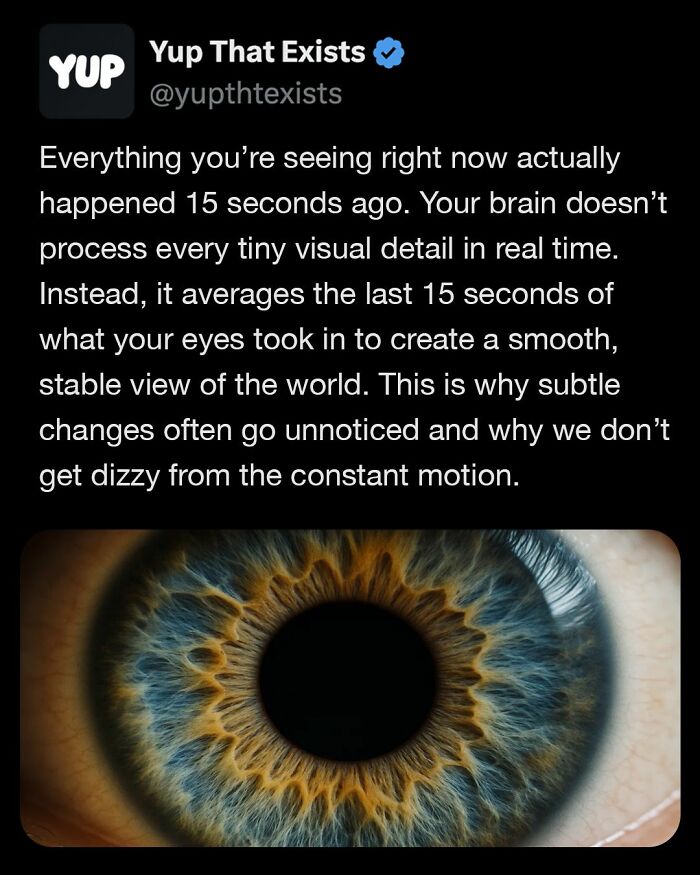
Image source: yupthatexists
#71

Image source: yupthatexists
#72
German engineers have just tested a hydrogen-powered jet engine that runs at full thrust without producing any carbon emissions.
The engine burns liquid hydrogen stored at super-cold temperatures and only releases water vapor. Special turbine blades and heat exchangers keep it running smoothly even at high altitudes.
While storing and fueling hydrogen is still tricky, the prototype already matches the power of modern jet engines. Backed by the European Union, this technology could turn commercial flights into zero-emission journeys and completely transform the future of air travel

Image source: yupthatexists
#73

Image source: yupthatexists
#74

Image source: yupthatexists
#75
A 28-year-old marketing manager from Malaysia, Farah Faizal, recently shared her deeply personal experience with a dramatic facial transformation during pregnancy. As she approached the final stages of her pregnancy, Farah’s face became severely inflamed, with deep wrinkles, an enlarged nose and ears, and pustules covering her skin.
Her usual skincare routine had no effect, and every morning brought new breakouts, leaving her feeling traumatized. Despite the challenges, she credits her husband with helping her maintain her mental health during this tough period.
After giving birth, Farah’s condition improved significantly, and a recent post shows the remarkable difference, most of the inflammation and pustules are gone.
While her story went viral, not all reactions were positive, with some accusing her of exaggerating or altering her photos. In response, Farah announced she’d no longer share updates about her condition, explaining that her goal was simply to highlight the often-overlooked physical and emotional toll pregnancy can take on women.

Image source: yupthatexists
#76

Image source: yupthatexists
#77

Image source: yupthatexists
#78
This photo shows a clever energy-saving escalator system used in Hong Kong. These escalators automatically slow down or stop when not in use, then start up again when someone steps on.
This smart feature can save around 60–70% of energy per unit compared to running nonstop, which adds up fast. On average, one escalator can save up to 7–10 kWh per day—that’s over 2,500–3,500 kWh per year. Multiply that by hundreds of escalators across the city, and you’re looking at massive energy and cost savings with a simple, efficient upgrade.

Image source: yupthatexists
#79
Cortical Labs has just taken computing to a whole new level with the CL1, the world’s first commercial biological computer powered by living human brain cells.
Using what the company calls Synthetic Biological Intelligence, this system combines organic neural networks with traditional hardware to create a type of intelligence that grows, learns, and evolves like a real brain.
The CL1 isn’t just fast or efficient, it adapts and thinks in ways silicon-based AI never could. This breakthrough could transform medical research, medicament discovery, robotics, and the future of AI by showing what’s possible when biology and technology merge.

Image source: yupthatexists
#80

Image source: yupthatexists
#81

Image source: yupthatexists
#82
Researchers from Harvard and MIT have developed a groundbreaking smart tattoo ink that could revolutionize health monitoring. This biosensitive ink changes color to alert users to potential health issues like dehydration or rising blood sugar levels.
The ink works by interacting with the body’s interstitial fluid, providing real-time data on glucose and sodium concentrations. Unlike traditional wearable devices, these tattoos don’t require batteries or wireless connections, offering a seamless, low-maintenance way to monitor health.
While still in the proof-of-concept phase, the technology holds immense potential for chronic condition monitoring and could even be used for temporary health checks or in astronauts. Once refined, this innovation could turn tattoos into powerful health monitors, sparking new conversations about how technology intersects with personal wellness.
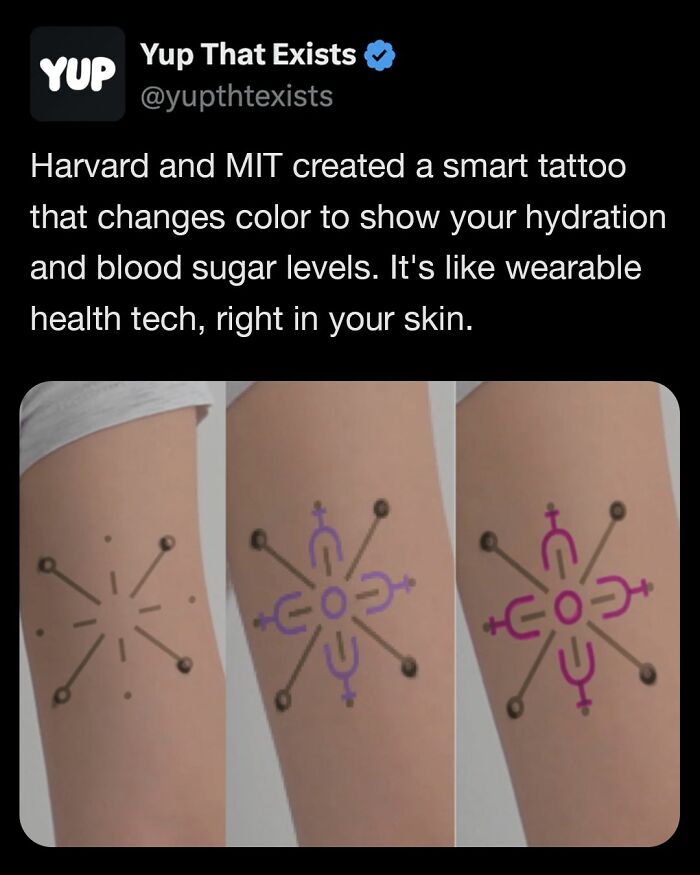
Image source: yupthatexists
#83

Image source: yupthatexists
#84

Image source: yupthatexists
#85
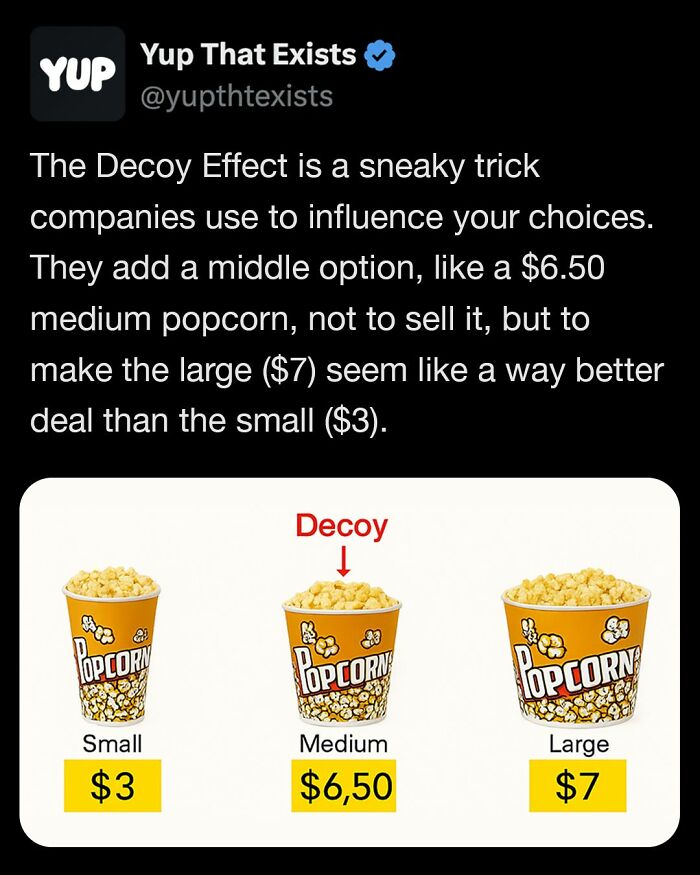
Image source: yupthatexists
#86
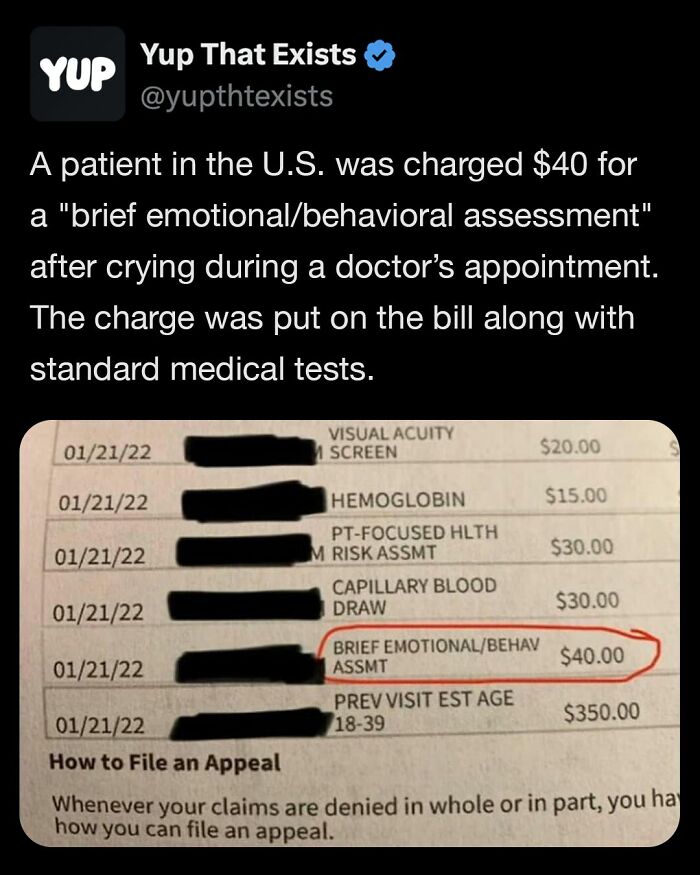
Image source: yupthatexists
#87
At one of the city’s public beaches, a small robot called BeBot quietly rolls across the sand, scooping up trash and debris. It’s just one of many new robots helping Detroit stay clean and efficient.
There’s Penny Pickup, a mobile bot that collects food waste from restaurants for composting. Snowbotix clears snow from icy sidewalks with a mini snow plow. Another bot even mows grass along highways, controlled remotely to keep workers safe. And if your electric car is running low, no worries: FlashBot is a rolling EV charger that comes right to you.
Detroit is embracing this robot revolution to improve city services and show off its tech talent. Once the heart of America’s auto industry, the city is now pushing into robotics and automation, giving its manufacturing roots a futuristic twist.
These friendly bots contrast with the more serious tech shown at a recent Detroit robotics summit, where defense companies showcased autonomous drones and robotic weaponry, highlighting the thin line between innovation and intimidation.

Image source: yupthatexists
#88

Image source: yupthatexists
#89

Image source: yupthatexists
#90
The bizarre changes are caused by a virus and scientists are investigating

Image source: yupthatexists
#91

Image source: yupthatexists
#92

Image source: yupthatexists
#93

Image source: yupthatexists
#94
The babirusa, found in Indonesia, is one of the strangest pigs you’ll ever hear about. What sets it apart are its massive tusks, which grow straight up through the top of its snout and then curve backwards toward its head like twisted horns.
These tusks aren’t used for digging or fighting, in fact, scientists still debate their true purpose. If the tusks don’t break or get worn down naturally, they can keep growing until they actually pierce the babirusa’s own skull. That means this animal can be fatally injured by its own teeth. It’s one of nature’s weirdest (and most unfortunate) design flaws

Image source: yupthatexists
#95
In a groundbreaking development, scientists are considering removing a second from global clocks in 2029 due to Earth’s increasing rotation speed.
Since 2020, the planet has been spinning slightly faster, shortening the length of a day by about 1.5 milliseconds. This may not sound like much, but over time, these small changes add up.
If the trend continues, it could lead to the first-ever “negative leap second,” essentially reversing the leap seconds that are occasionally added to account for irregularities in Earth’s rotation.
While the need for a negative leap second is not guaranteed, it reflects a fascinating shift in how we measure time. If it happens, it will be a milestone in our understanding of Earth’s mechanics and how human timekeeping interacts with natural forces.

Image source: yupthatexists
#96
A Tokyo-based tech company has announced a groundbreaking achievement: the creation of the world’s first drone capable of triggering and guiding lightning strikes. This innovative drone reportedly works like a flying lightning rod, drawing electricity from thunderclouds while remaining airborne, with minimal damage to its structure. While these claims are still unverified, the technology could have significant implications for protecting cities and infrastructure from lightning-related damage.
Every minute, approximately 6,000 lightning strikes hit the Earth, wreaking havoc by sparking fires, triggering explosions, and causing power surges that damage electrical systems. While lightning rods provide some protection, this drone aims to offer a more advanced solution. In December 2024, the drone successfully flew into a storm in Japan’s Shimane prefecture, attaching itself to a conductive wire that triggered a lightning strike. Despite its protective covering melting, the drone kept flying.
The concept of using technology to attract lightning isn’t new—scientists have tested lasers for this purpose—but the NTT group’s drone uses a Faraday cage to protect it from the electrical damage. Although the company envisions using drones to safely guide lightning away from infrastructure, they’re also exploring the possibility of harnessing lightning’s power for energy—though this remains theoretical for now. If proven successful, the drone could be a game-changer in lightning protection and energy innovation.

Image source: yupthatexists
#97
A robotics company in China is reportedly on the verge of completing the world’s first humanoid pregnancy robot, and it’s already stirring up intense debate online.
The robot, developed by Kaiwa Technology, features an artificial womb inside a robotic abdominal module that could carry a full 10-month pregnancy and even give birth to a live baby. According to CEO Zhang Qifeng, animal tests have been promising, and the humanoid surrogate could hit the market within a year for under $14,000.
The concept has divided social media users, with some hailing it as a breakthrough for people struggling to conceive, while others call it unnatural and unethical. Experts remain cautious, pointing out that replicating the complex hormonal, immune, and neurological aspects of human pregnancy is far from guaranteed

Image source: yupthatexists
#98
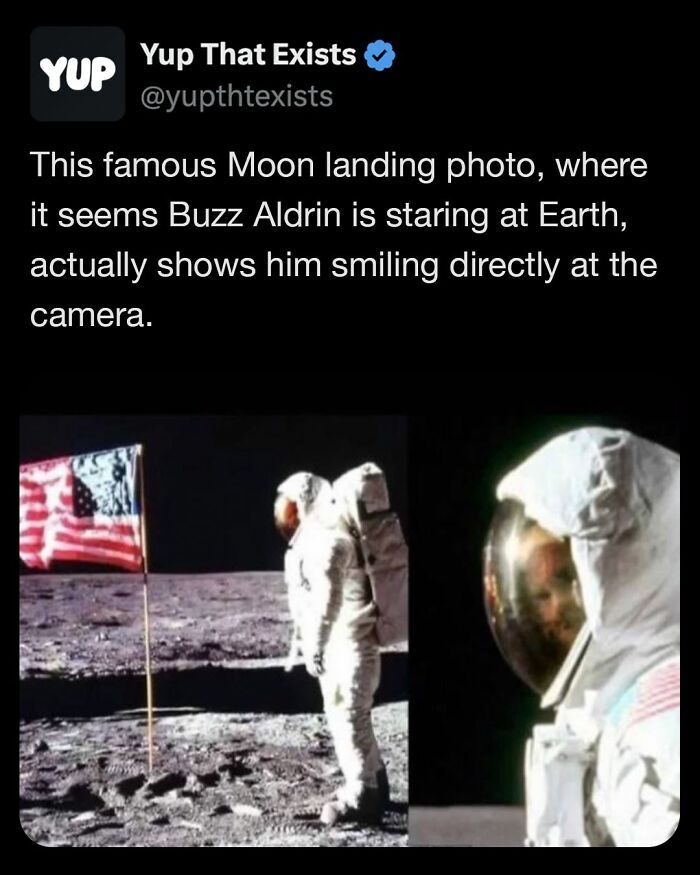
Image source: yupthatexists
#99

Image source: yupthatexists
#100

Image source: yupthatexists
#101

Image source: yupthatexists
#102

Image source: yupthatexists
#103
A groundbreaking new surveillance method is using Wi-Fi signals to identify and track people, without the need for phones, cameras, or wearables.
Created by researchers at La Sapienza University of Rome, this innovative system called “WhoFi” works by reading how Wi-Fi waves interact with the human body, essentially generating a unique biometric “fingerprint.”
This allows individuals to be recognized and tracked across rooms or even different locations, all without any visible technology or consent. Unlike previous tracking attempts, WhoFi uses neural networks and low-cost Wi-Fi routers to achieve remarkable accuracy.
While the technology is still in its experimental phase, its ability to work through walls and in the dark could have massive implications, especially in fields like retail and law enforcement, sparking major privacy concerns.

Image source: yupthatexists
#104
Image source: yupthatexists
#105
Rather than drilling through the mountains or building around them, engineers decided to literally shave off parts of the mountains to make way for this massive road. The expressway, which leads to the upcoming Huajiang Grand Canyon Bridge (the world’s highest at 625 meters), has recently gone viral, sparking debates across social media.
While some are amazed by the feat of engineering, others are concerned about the environmental impact of carving through such a rugged landscape. Guizhou, known for its mountainous terrain, could benefit from better roads, but critics argue there might have been less extreme alternatives.
The discussion continues to heat up, with opinions split between admiration for the infrastructure and worries about the ecological cost.

Image source: yupthatexists
#106

Image source: yupthatexists
#107

Image source: yupthatexists
#108

Image source: yupthatexists
#109

Image source: yupthatexists
 Follow Us
Follow Us





